Mutability Difference:
String is immutable, if you try to alter their values, another object gets created, whereas StringBuffer and StringBuilder are mutable so they can change their values.
Thread-Safety Difference:
The difference between
StringBuffer and StringBuilder is that StringBuffer is thread-safe. So when the application needs to be run only in a single thread then it is better to use StringBuilder. StringBuilder is more efficient than StringBuffer.
Situations:
- If your string is not going to change use a String class because a
Stringobject is immutable. - If your string can change (example: lots of logic and operations in the construction of the string) and will only be accessed from a single thread, using a
StringBuilderis good enough. - If your string can change, and will be accessed from multiple threads, use a
StringBufferbecauseStringBufferis synchronous so you have thread-safety.
transient
is a Java keyword which marks a member variable not to be serialized when it is persisted to streams of bytes.
When an object is transferred through the network, the object needs to be 'serialized'. Serialization converts the object state to serial bytes. Those bytes are sent over the network and the object is recreated from those bytes. Member variables marked by the java
transient keyword are not transferred; they are lost intentionally.Serialization in Java
Serialization in java is a mechanism of writing the state of an object into a byte stream.
It is mainly used in Hibernate, RMI, JPA, EJB and JMS technologies.
The reverse operation of serialization is called deserialization.
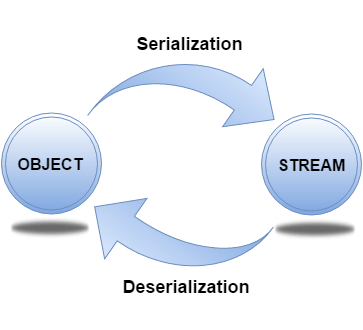
It is mainly used to travel object's state on the network (known as marshaling).
java.io.Serializable interface
Serializable is a marker interface (has no data member and method). It is used to "mark" java classes so that objects of these classes may get certain capability. The Cloneable and Remote are also marker interfaces.
-->public class Student implements Serializable
eg:
- import java.io.Serializable;
- public class Student implements Serializable{
- int id;
- String name;
- public Student(int id, String name) {
- this.id = id;
- this.name = name;
- }
- }
No comments:
Post a Comment